skin diagnosis
What is meant by oily skin?
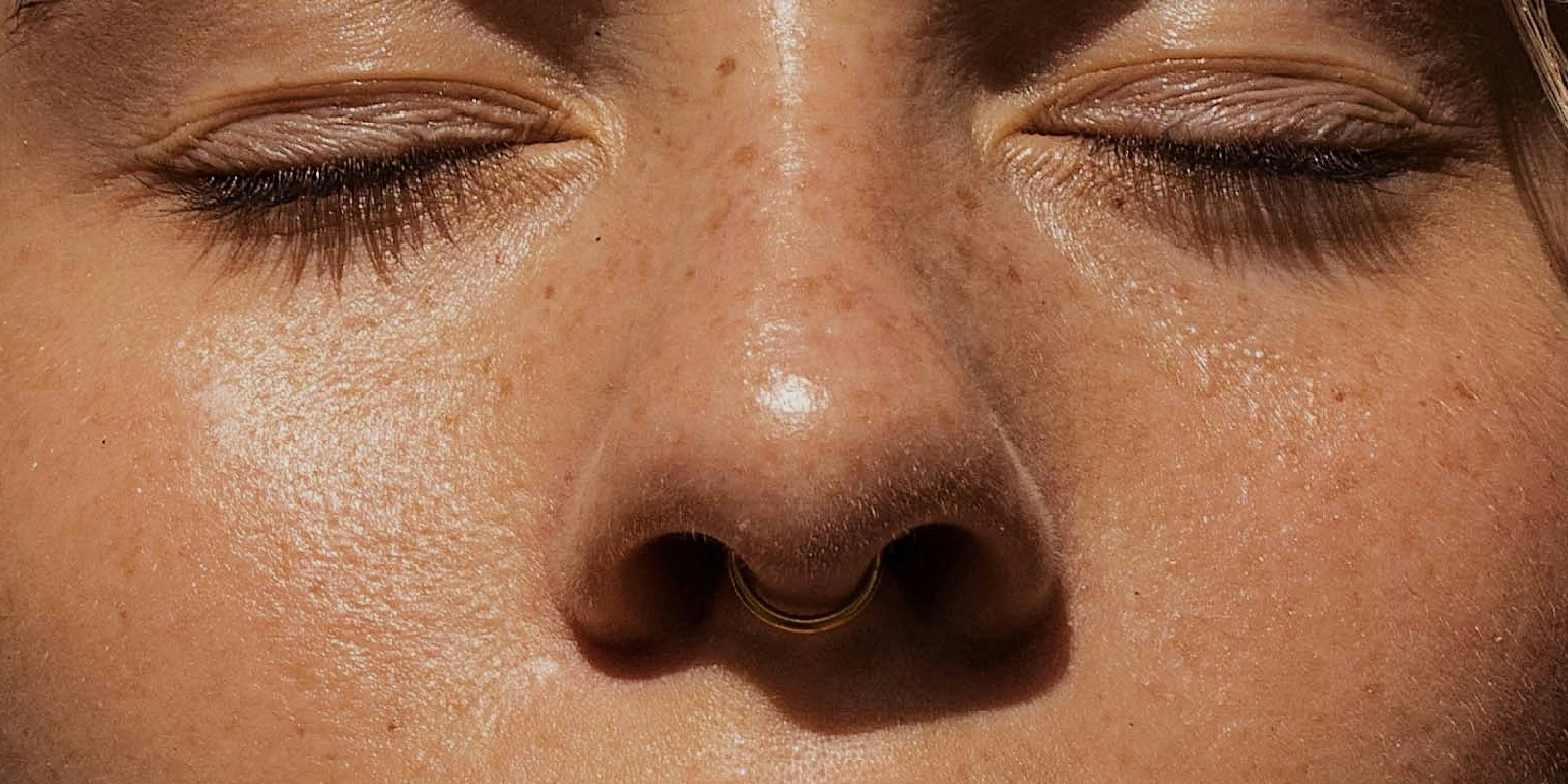
Understanding Skin Condition
Oily skin is a skin type in which the sebaceous glands produce excessive amounts of sebum. This often causes the skin to appear shiny, especially in the T-zone (forehead, nose, chin), and is prone to enlarged pores, blackheads, and blemishes.
Despite the greasy film, oily skin can also lack moisture – therefore, balancing, non-drying care is particularly important.
The right care for oily skin
Gentle cleansing
The foundation of any skincare routine is a gentle yet thorough cleansing routine. Cleansing products for oily skin should be oil-free, non-comedogenic, and pH-balanced. Gel or foam cleansers are best, as they remove excess sebum without irritating the skin barrier. Important: Cleanse in the morning and evening—but not more often to avoid overproduction of sebum.
Tonic & Serums
After cleansing, a clarifying toner is ideal for tightening pores and preparing the skin for skincare. Active ingredients like niacinamide, zinc, or salicylic acid (BHA) have a regulating and anti-inflammatory effect—perfect for oily or blemish-prone skin. Light serums with moisturizing ingredients like hyaluronic acid or aloe vera also give the skin exactly what it needs—without weighing it down.
moisturizing
A common mistake: not applying any moisturizer to oily skin. But oily skin needs moisture too! The right texture is key – light creams or fluid care products nourish the skin without causing shine. Many special formulations for oily skin also have a mattifying effect and help even out the complexion in the long term.
UV protection
Even with oily skin, daily sun protection is a must. Modern sunscreens with a light, oil-free texture reliably protect the skin without making it look greasy or clogging pores.
Evening care
In the evening, your skincare routine can be a bit more active. Serums with AHA/BHA acids help remove dead skin cells, unclog pores, and reduce impurities. Products containing retinol can also regulate sebum production in the long term—assuming your skin isn't hypersensitive.
The foundation of any skincare routine is a gentle yet thorough cleansing routine. Cleansing products for oily skin should be oil-free, non-comedogenic, and pH-balanced. Gel or foam cleansers are best, as they remove excess sebum without irritating the skin barrier. Important: Cleanse in the morning and evening—but not more often to avoid overproduction of sebum.
After cleansing, a clarifying toner is ideal for tightening pores and preparing the skin for skincare. Active ingredients like niacinamide, zinc, or salicylic acid (BHA) have a regulating and anti-inflammatory effect—perfect for oily or blemish-prone skin. Light serums with moisturizing ingredients like hyaluronic acid or aloe vera also give the skin exactly what it needs—without weighing it down.
A common mistake: not applying any moisturizer to oily skin. But oily skin needs moisture too! The right texture is key – light creams or fluid care products nourish the skin without causing shine. Many special formulations for oily skin also have a mattifying effect and help even out the complexion in the long term.
Even with oily skin, daily sun protection is a must. Modern sunscreens with a light, oil-free texture reliably protect the skin without making it look greasy or clogging pores.
In the evening, your skincare routine can be a bit more active. Serums with AHA/BHA acids help remove dead skin cells, unclog pores, and reduce impurities. Products containing retinol can also regulate sebum production in the long term—assuming your skin isn't hypersensitive.
Supporting the skin in everyday life
Nutrition: Your diet plays a key role in maintaining a balanced complexion. A skin-friendly diet for oily skin is rich in fresh vegetables, fruit, and healthy fats—such as nuts, linseed oil, or avocados. These provide important vitamins, minerals, and omega-3 fatty acids, which can reduce inflammation and soothe the skin. At the same time, it's worth reducing highly processed foods, high-sugar products, and excessive dairy consumption, as these can promote sebum production and increase the risk of blemishes. Drinking enough fluids—ideally water or unsweetened tea—also supports the skin's metabolism from within.
Hygiene: Especially for oily skin, a clean environment is important without unnecessarily irritating the skin. Wash your face twice a day with a mild cleansing gel – washing too often or aggressively can dry out the skin and thus even stimulate sebum production. Also pay attention to small but effective hygiene measures: wash your hands regularly, touch your face as little as possible, change pillows and towels frequently, and even clean your smartphone regularly. All of this reduces the bacterial load on your skin and can help prevent blemishes.
Environmental factors: UV radiation, air pollution, and air conditioning put a strain on the skin every day – especially on oily skin, these factors can disrupt its balance. Therefore, even if you have oily skin, use a light sunscreen daily, preferably with an oil-free formula. In the evening, it's especially important to thoroughly cleanse your skin to remove dirt, sebum, makeup, and environmental residues. This allows it to regenerate and prevent new blemishes from forming.
Stress management: Stress is one of the often underestimated causes of oily skin and blemishes. It affects hormonal balance, increases sebum production, and can exacerbate inflammatory processes. This makes it all the more important to consciously find time to relax regularly. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, or breathing exercises help you find inner balance—which can have a positive effect on your skin. Exercise also regulates stress hormones: A walk in the fresh air or a yoga session can work wonders—for your body, mind, and skin.
Sleep: At night, your skin works at full speed. It regenerates, repairs, and balances itself. That's why sufficient and restful sleep is essential—not only for your well-being, but also for a clear, fresh complexion. Those who consistently lack sleep not only risk dark circles under the eyes, but also increased inflammation and oilier skin. Aim to get 7–9 hours of sleep per night—ideally in a quiet, dark room and with a consistent evening routine.
Avoid skin saboteurs in everyday life: In addition to the factors mentioned above, there are also things that can aggravate oily skin—without us always being consciously aware of them. These include nicotine, excessive alcohol consumption, too much caffeine, or constant stress from constant overstimulation (e.g., from social media, work, or constant availability). Those who manage to consciously counteract these factors not only support their mental health but also their skin's long-term appearance.
Causes of oily skin

Internal influencing factors
Hormonal changes are often one of the causes of oily skin.
Hormonal changes are among the most common causes of oily skin. They directly influence sebum production—the amount of skin oil secreted by our sebaceous glands. If the hormonal imbalance is disrupted, the skin often produces too much sebum, which can lead to shine, enlarged pores, and blemishes. Androgens (male sex hormones that also occur in the female body) play a particularly central role here.
- Puberty: During puberty, androgen levels (male sex hormones that also occur in women) rise sharply. These hormones stimulate the sebaceous glands to produce more sebum. This explains why adolescents often suffer from oily skin, blackheads, or acne. For many, their skin condition normalizes with the end of puberty – but for some, oily skin persists into adulthood.
- Pregnancy: During pregnancy, the appearance of your skin can change dramatically. Some women experience significant improvement, while others suddenly struggle with oily, blemished skin. The changing hormone levels—especially the increased androgens—can cause the sebaceous glands to overactive, leading to increased shine and blemishes.
- Menopause: During menopause, estrogen levels drop significantly. Estrogen regulates sebum production. The decline in hormones can therefore paradoxically lead to increasingly oily skin in some women, especially if there is a concurrent relative increase in androgens. Others, however, experience dry skin. Both are possible – depending on the individual's hormonal balance.
- Menstrual cycle: Hormones also affect the skin in adulthood. Many women notice oilier skin shortly before their period—especially in the T-zone. The reason: The rise in progesterone in the second half of the cycle can increase sebum production. After the period, when estrogen levels rise again, the skin often appears clearer and less oily.
- Contraceptives: Hormonal contraceptives like the pill can affect the skin's appearance – and the effects can vary greatly depending on their composition. Some products contain antiandrogenic active ingredients that reduce sebum production and thus improve oily skin. Others can alter the hormonal balance, causing skin to become oilier or more troubled – especially when stopping or changing products.
Other internal factors can affect oily skin:
Genetic predisposition: Some people naturally have a more active sebum production. If oily skin runs in the family, the likelihood of being affected is higher.
Hormonal imbalances: Diseases such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or thyroid problems can lead to permanently increased sebum production and impure skin.

External influencing factors
While internal causes play a role, external influences can further strain skin health. It's important to recognize these factors and take targeted measures.
Environmental factors, medications, diet, and stress can all contribute to oily skin.
- Diet and lifestyle: Although not exclusively internal, but closely linked – a diet that is very high in sugar or fat can influence hormonal processes and promote oily skin.
- Stress: Persistent stress increases cortisol levels in the body. Cortisol can promote inflammation and stimulate the sebaceous glands—a common cause of suddenly oily, troubled skin.
- Medications: Certain medications such as steroids or hormone therapies can cause oily skin as a side effect.
Incorrect skin care: is a common but preventable cause of oily skin. Those who use harsh, drying, or over-conditioning products can easily throw their skin off balance. A gentle, balancing skincare routine that regulates sebum without irritating the skin is better. This will make oily skin calmer, clearer—and healthier—in the long run.
Internal influencing factors
Hormonal changes are often one of the causes of oily skin.
Hormonal changes are among the most common causes of oily skin. They directly influence sebum production—the amount of skin oil secreted by our sebaceous glands. If the hormonal imbalance is disrupted, the skin often produces too much sebum, which can lead to shine, enlarged pores, and blemishes. Androgens (male sex hormones that also occur in the female body) play a particularly central role here.
- Puberty: During puberty, androgen levels (male sex hormones that also occur in women) rise sharply. These hormones stimulate the sebaceous glands to produce more sebum. This explains why adolescents often suffer from oily skin, blackheads, or acne. For many, their skin condition normalizes with the end of puberty – but for some, oily skin persists into adulthood.
- Pregnancy: During pregnancy, the appearance of your skin can change dramatically. Some women experience significant improvement, while others suddenly struggle with oily, blemished skin. The changing hormone levels—especially the increased androgens—can cause the sebaceous glands to overactive, leading to increased shine and blemishes.
- Menopause: During menopause, estrogen levels drop significantly. Estrogen regulates sebum production. The decline in hormones can therefore paradoxically lead to increasingly oily skin in some women, especially if there is a concurrent relative increase in androgens. Others, however, experience dry skin. Both are possible – depending on the individual's hormonal balance.
- Menstrual cycle: Hormones also affect the skin in adulthood. Many women notice oilier skin shortly before their period—especially in the T-zone. The reason: The rise in progesterone in the second half of the cycle can increase sebum production. After the period, when estrogen levels rise again, the skin often appears clearer and less oily.
- Contraceptives: Hormonal contraceptives like the pill can affect the skin's appearance – and the effects can vary greatly depending on their composition. Some products contain antiandrogenic active ingredients that reduce sebum production and thus improve oily skin. Others can alter the hormonal balance, causing skin to become oilier or more troubled – especially when stopping or changing products.
Other internal factors can affect oily skin:
Genetic predisposition: Some people naturally have a more active sebum production. If oily skin runs in the family, the likelihood of being affected is higher.
Hormonal imbalances: Diseases such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or thyroid problems can lead to permanently increased sebum production and impure skin.
External influencing factors
While internal causes play a role, external influences can further strain skin health. It's important to recognize these factors and take targeted measures.
Environmental factors, medications, diet, and stress can all contribute to oily skin.
- Diet and lifestyle: Although not exclusively internal, but closely linked – a diet that is very high in sugar or fat can influence hormonal processes and promote oily skin.
- Stress: Persistent stress increases cortisol levels in the body. Cortisol can promote inflammation and stimulate the sebaceous glands—a common cause of suddenly oily, troubled skin.
- Medications: Certain medications such as steroids or hormone therapies can cause oily skin as a side effect.
Incorrect skin care: is a common but preventable cause of oily skin. Those who use harsh, drying, or over-conditioning products can easily throw their skin off balance. A gentle, balancing skincare routine that regulates sebum without irritating the skin is better. This will make oily skin calmer, clearer—and healthier—in the long run.


Recognize common features
First signs of oily skin
Oily skin is usually easy to recognize – especially if you know what to look for. Typical is a visible shine, which increases particularly during the day. Particularly affected is the so-called T-zone – forehead, nose and chin – because there are particularly many sebaceous glands here.
Another clear feature is enlarged, often visible pores, which are dilated by the increased sebum production. In many cases, Impurities such as blackheads, pimples or inflamed areas, as excess sebum can clog the pores.
The difference is also evident in the skin’s feel: Oily skin quickly feels heavy or greasy especially after waking up or in the afternoon. Makeup often stays on less well and "slips" over the course of the day because the skin releases more oil to the surface than other skin types.
It is important to note that even though oily skin is often associated with impurities, it can also lack of moisture. This can be seen in the form of tightness or dry patches despite the shine. Therefore, oily skin also needs well-coordinated, moisturizing care that doesn't complain.
Frequency of oily skin in different stages of life
Frequency: Approximately 30–50% of the population suffer from oily skin throughout their lives. Adolescents and young adults are particularly affected – in women between 20 and 30 years of age, the incidence in some regions is over 50%. Oily skin is particularly common in warmer climates and urban areas.
Age: Sebum production is particularly active in young people. Studies show that up to 40% of those under 30 have oily skin. With increasing age, sebum production decreases – only about 20% of those over 60 are affected. Hormonal fluctuations (e.g., puberty, pregnancy, menstruation) also play a role.
Causes: Oily skin is caused by Overproduction of sebum (skin oil) Genetics, hormones, diet, improper skincare products (e.g., drying cleansers), environmental factors such as heat and air pollution, and stress can further stimulate sebum production.
Effects: Oily skin is often associated with enlarged pores, Blackheads, Skin blemishes and a lasting shine associated – especially in the T-zone. 15–25% of those affected report psychological stress caused by their skin, especially when there are very visible blemishes.
Treatment:Targeted skin care with sebum-regulating, but moisturizing products are crucial. Active ingredients such as Niacinamide, zinc, Salicylic acid or light moisturizers like aloe vera are particularly effective. 80% of those affected regularly use special cleaning or care products for oily skin.
Combination with other skin problems: Oily skin often occurs together with acne, clogged pores or sensitive combination skin. Hormonal skin changes (e.g., PMS or PCOS) can also worsen oily skin.
Cost: In Europe alone, several hundred million euros are spent annually on products to regulate oily skin and treat blemishes. In the USA, the market for acne and oil-free skin care products is over 1 billion USD per year.
Prevention: The best prevention is mild cleaning,non-comedogenic care products and a conscious lifestyle Stress management, a balanced diet, and daily UV protection help regulate sebum production in the long term and improve the skin's appearance.







































